
In today’s interconnected world, where information flows freely and technology advancements abound, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. As organizations and individuals rely more on digital systems and networks to store and transmit sensitive data, the risks and challenges associated with cyber threats continue to grow at an alarming rate. The increasing reliance on digital infrastructure, cloud services, and interconnected devices has expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals, making it crucial to stay ahead of evolving risks. To effectively protect sensitive data, intellectual property, and personal information, it is essential to have a deep understanding of emerging trends in cybersecurity. as technology continues to advance, the cybersecurity landscape will continue to evolve. By understanding and embracing emerging trends, organizations and individuals can better protect themselves against the ever-growing range of cyber threats. Proactive measures, such as staying informed, investing in advanced security solutions, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity, will be essential for safeguarding sensitive data and mitigating risks in the interconnected world we live in today. In this blog, we will explore some key trends in cybersecurity that will shape the future of cyberworld, enabling organizations and individuals to proactively address the evolving threat landscape.

Artificial intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing the cybersecurity landscape. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, detect anomalies, and identify potential threats in real time. Moreover, AI-powered cybersecurity systems can adapt to and learn from new attack patterns, enabling proactive defense mechanisms. Additionally, by leveraging AI and machine learning, cybersecurity professionals can automate routine tasks, freeing up time for more strategic and complex security initiatives. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into the cybersecurity landscape brings transformative capabilities. These technologies empower organizations to detect and respond to threats in real time, automate routine tasks, and improve incident response and recovery. By harnessing the power of AI, cybersecurity professionals can enhance their ability to protect sensitive data and systems in an increasingly complex and evolving threat landscape.

As the number of connected devices continues to grow, IoT security becomes increasingly critical. The interconnectivity of devices presents a broader attack surface, making them potential entry points for cybercriminals. Furthermore, securing IoT devices requires robust authentication protocols, encryption techniques, and proactive monitoring to prevent potential vulnerabilities from being exploited. Moreover, as IoT devices become more ubiquitous in our daily lives, the need for comprehensive security measures, including regular updates and patches, is vital to protect both personal and organizational data. In addition to the growing number of connected devices, the expanding use of IoT technology in various sectors such as healthcare, manufacturing, and smart homes further emphasizes the significance of IoT security. For instance, in healthcare, IoT devices are used to monitor patients, track vital signs, and manage medical equipment. Any compromise in the security of these devices could have severe consequences, including the unauthorized access or alteration of patient data, disruption of critical healthcare services, or even potential harm to patients’ well-being.

The migration of data and services to the cloud brings its own set of security challenges. Organizations need to ensure that their cloud environments are adequately protected. Additionally, organizations must prioritize cloud security by implementing strong access controls, encryption, and continuous monitoring to protect sensitive information stored in cloud environments. Furthermore, organizations should collaborate with cloud service providers to establish shared responsibility models, where both parties work together to maintain a secure cloud infrastructure. To enhance cloud security further, organizations should establish strong partnerships and collaborations with their cloud service providers. By working together, both parties can establish shared responsibility models, where the organization and the provider each have defined roles and responsibilities for maintaining a secure cloud infrastructure. This collaboration ensures that security measures are effectively implemented and maintained throughout the cloud ecosystem.

The traditional perimeter-based security approach is no longer sufficient in today’s dynamic threat landscape. Organizations are moving towards a Zero Trust Architecture model. This model assumes that no user or device should be inherently trusted, requiring continuous verification and authentication throughout the network. Implementing a Zero Trust Architecture approach involves several key components. One crucial element is the adoption of multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA strengthens security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as passwords, biometrics, or security tokens, ensuring that even if one factor is compromised, the attacker cannot gain unauthorized access. Moreover, a Zero Trust Architecture approach aligns well with modern work environments, including remote and mobile workforce scenarios. As organizations increasingly embrace flexible work arrangements, a Zero Trust Architecture ensures that access controls and security measures are consistently applied, regardless of the user’s location or device.
Quantum computing poses a significant threat to current encryption methods, as its computational power has the potential to break traditional cryptographic algorithms. This technological advancement has raised concerns about the future security of sensitive data and communications. However, researchers and experts in the field of cryptography are actively working on developing post-quantum cryptography, which aims to provide secure encryption algorithms that can withstand attacks from quantum computers. The focus of post-quantum cryptography is to develop encryption techniques that are resistant to attacks by quantum computers. These algorithms are designed to be secure against both classical and quantum computing threats, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected in the post-quantum era. By leveraging mathematical problems that are difficult for quantum computers to solve, such as lattice-based or code-based cryptography, researchers are exploring new encryption alternatives that can withstand quantum attacks.
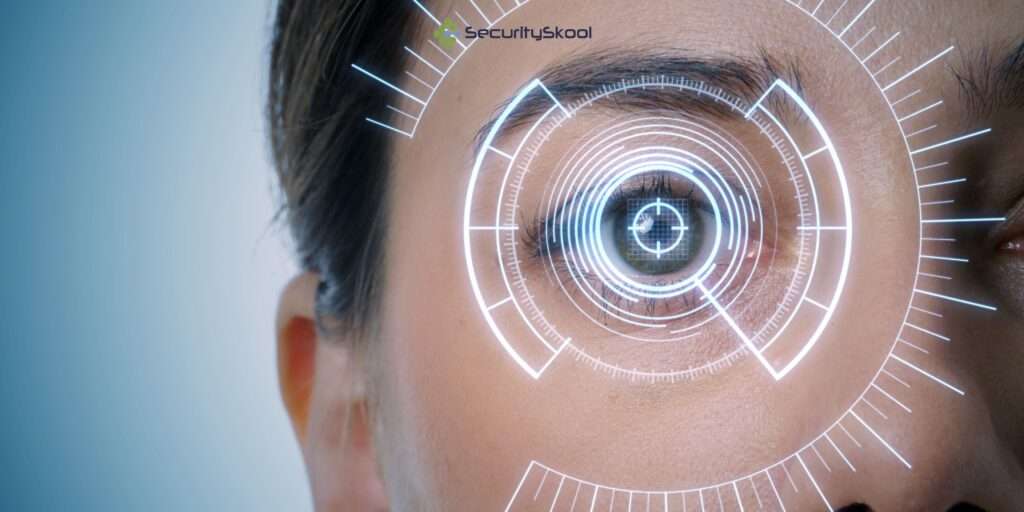
Biometric authentication, including fingerprint or facial recognition, is gaining popularity as an added layer of security. By utilizing unique and personal identifiers, it enhances access control measures and reduces the risk of unauthorized access. However, as biometric authentication becomes more widespread in devices and applications, it is essential to prioritize the privacy and protection of biometric data. To safeguard biometric data, organizations must implement stringent measures. This includes employing robust encryption techniques and secure storage methods to prevent unauthorized access or tampering. It is also crucial to comply with relevant privacy regulations, ensuring that the collection, use, and storage of biometric data align with legal requirements and industry standards. By effectively securing biometric authentication systems, organizations can leverage the benefits of this technology while ensuring the privacy and protection of individuals’ biometric data.
In conclusion, as technology continues to advance, the cybersecurity landscape will continue to evolve. By understanding and embracing emerging trends in cybersecurity, organizations and individuals can better protect themselves against the ever-growing range of cyber threats. Proactive measures, such as staying informed, investing in advanced security solutions, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity, will be essential for safeguarding sensitive data and mitigating risks in the interconnected world we live in today.
WhatsApp us